Are you looking to improve your overall health and prevent various diseases? Well, physical fitness is key! It plays such a vital role in keeping your body in tip-top shape. Have you ever wondered how physical fitness can benefit you besides just helping you look good? In this article, we will delve deeper into the topic and explore the many ways physical fitness can contribute to disease prevention. Let’s get started!
Physical fitness involves engaging in regular physical activity that gets your heart pumping and your muscles working. This could be anything from running, swimming, or even dancing. The important thing is to find an activity that you enjoy and can sustain over time. The benefits of physical fitness go far beyond just helping you fit into your favorite jeans. Regular exercise has been shown to boost your immune system, reducing your risk of getting sick. It also helps improve your cardiovascular health, lowering your chances of developing heart disease. In addition, physical fitness can help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By engaging in regular exercise, you are taking a proactive step towards preventing diseases and staying healthy. So, keep reading to learn more about how physical fitness can benefit you in the long run! and disease prevention go hand in hand. Engaging in regular physical activity has numerous benefits for both your body and mind. In this article, we will explore the various benefits of physical fitness, the components of physical fitness, the role of physical fitness in disease prevention, recommendations for physical fitness, the effects of a sedentary lifestyle on health, the relationship between physical fitness and mental health, the impact of physical fitness on aging, promoting physical fitness in children and adolescents, physical fitness for different population groups, and conclude with the importance of regular physical activity for overall well-being.
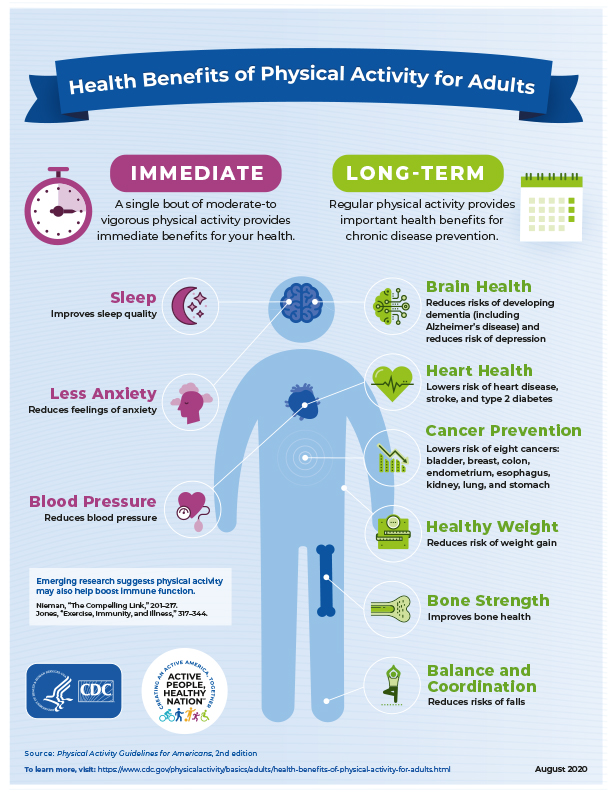
Benefits of Physical Fitness
Reduced risk of chronic diseases
One of the most significant benefits of physical fitness is the reduced risk of chronic diseases. Regular exercise can help prevent and manage conditions such as heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Adopting a physically active lifestyle can go a long way in preventing the onset of these diseases, as well as improving outcomes for those already affected.
Improved mental health
Physical fitness also plays a vital role in improving mental health. Engaging in regular exercise has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, boost mood, enhance self-esteem, and improve overall mental well-being. Physical activity stimulates the release of endorphins, commonly known as “feel-good” hormones, which contribute to improved mood and mental clarity.
Enhanced cardiovascular health
Engaging in regular physical activity improves cardiovascular health by strengthening the heart and improving blood flow. Aerobic exercises such as running, swimming, or cycling increase heart rate and oxygen consumption, leading to improved cardiovascular endurance. A healthier cardiovascular system reduces the risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.
Increased longevity
Regular physical activity has been linked to increased longevity. Leading an active lifestyle can prevent premature death by reducing the risk of various diseases and promoting overall health and well-being. Studies have shown that individuals who participate in regular physical activity live longer, enjoy a higher quality of life, and are more likely to maintain their independence as they age.
Components of Physical Fitness
Physical fitness comprises several components that contribute to overall health and well-being. These components include:
Cardiorespiratory endurance
Cardiorespiratory endurance refers to the ability of the heart, lungs, and circulatory system to provide oxygen and energy to the muscles during physical activity. Engaging in aerobic exercises such as jogging, swimming, or cycling improves cardiorespiratory endurance, allowing individuals to engage in prolonged physical activities without excessive fatigue.
Muscular strength
Muscular strength is the maximum amount of force that a muscle or group of muscles can exert against resistance. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or resistance training, help build muscular strength. Having stronger muscles not only improves physical performance but also helps protect against injuries and reduces the risk of muscle imbalances.
Muscular endurance
Muscular endurance refers to the ability of a muscle or group of muscles to sustain repeated contractions over an extended period. Activities such as push-ups, sit-ups, or planks improve muscular endurance. Building muscular endurance allows individuals to perform tasks and activities for longer periods without experiencing muscle fatigue.
Flexibility
Flexibility refers to the range of motion in a joint or group of joints. Stretching exercises, yoga, or Pilates can improve flexibility. Maintaining good flexibility helps prevent muscle imbalances, reduces the risk of injuries during physical activity, and enhances overall mobility.
Body composition
Body composition refers to the ratio of lean body mass (muscles, bones, organs) to body fat. Engaging in regular physical activity, along with a balanced diet, can help achieve and maintain a healthy body composition. Maintaining a healthy body composition is important for overall health and reduces the risk of obesity and related diseases.
Role of Physical Fitness in Disease Prevention
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in disease prevention. By incorporating exercise into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of various health conditions, including:
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Engaging in regular aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, helps strengthen the heart and improve blood circulation. Regular physical activity can lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and prevent the development of heart diseases such as coronary artery disease and heart attacks.
Lowered risk of diabetes
Physical fitness plays a significant role in diabetes prevention and management. Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use glucose more effectively. This reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and helps individuals with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels better.
Decreased likelihood of obesity
Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy body weight and reduces the likelihood of obesity. Obesity is a significant risk factor for various chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Engaging in regular exercise, along with a balanced diet, promotes weight loss or weight maintenance, reducing the risk of obesity-related complications.
Reduced risk of certain cancers
Studies have shown that physical activity can reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including colon, breast, and lung cancer. Regular exercise may help regulate hormone levels, boost the immune system, reduce inflammation, and support overall cellular health, reducing the risk of cancer development.
Physical Fitness Recommendations
To achieve and maintain physical fitness, it is recommended to incorporate various types of exercise into your routine. Here are some guidelines:
Guidelines for aerobic exercise
The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. This can be achieved through activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming. It is important to spread the exercise throughout the week and engage in activities that you enjoy.
Strength training recommendations
The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommend engaging in strength training exercises at least two days per week. Strength training can be done using resistance bands, free weights, weight machines, or bodyweight exercises such as push-ups, squats, and lunges. Aim to work all major muscle groups, including the legs, arms, chest, back, shoulders, and core.
Flexibility exercises
Stretching exercises should be included in your fitness routine to improve flexibility and prevent injuries. Perform stretching exercises for major muscle groups at least two to three times per week. Yoga or Pilates classes are also great options for improving flexibility and overall body strength.
Importance of rest and recovery
Incorporating rest and recovery days into your fitness routine is essential for preventing injuries and allowing your body to heal and rebuild. Overtraining can lead to decreased performance and increased risk of injuries. Aim for at least one or two rest days per week to allow your body to recover and rejuvenate.
Effects of Sedentary Lifestyle on Health
Leading a sedentary lifestyle, characterized by a lack of physical activity and excessive sitting, has detrimental effects on health. Some of the consequences of a sedentary lifestyle include:
Increased risk of chronic diseases
A sedentary lifestyle is associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. Prolonged sitting and physical inactivity can lead to weight gain, poor cardiovascular health, and an increased likelihood of developing various health conditions.
Negative impact on mental well-being
Sedentary behavior has also been linked to negative effects on mental well-being. Spending long hours sitting or lying down can contribute to feelings of lethargy, decreased motivation, and increased symptoms of anxiety and depression. Engaging in regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining good mental health.
Muscle and bone health issues
Lack of physical activity and prolonged sitting can lead to muscle and bone health problems. Muscles become weaker and more prone to injuries when not regularly used. Additionally, sedentary behavior contributes to bone loss and decreased bone density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
Physical Fitness and Mental Health
Engaging in regular physical activity can have a significant positive impact on mental health. Here’s how physical fitness benefits your mental well-being:
Reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety
Physical activity has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, which act as natural mood boosters and help alleviate feelings of sadness and anxiety. Engaging in regular physical activity can improve overall mood and contribute to a positive sense of well-being.
Improved cognitive function
Physical fitness is closely linked to improved cognitive function. Regular exercise increases blood flow to the brain, promotes the growth of new neurons, and enhances synaptic plasticity. This leads to improved memory, concentration, and overall mental clarity.
Enhanced self-esteem and body image
Regular physical activity can improve self-esteem and body image. Engaging in exercise helps individuals feel more confident in their abilities and physical appearance. Achieving fitness goals, such as running a marathon or gaining strength, can boost self-esteem and promote a positive body image.
Physical Fitness and Aging
Physical fitness plays a vital role in managing age-related health issues, maintaining independence, and improving the overall quality of life in older adults. Here’s how physical fitness impacts aging:
Management of age-related health issues
Engaging in regular physical activity can help manage age-related health issues such as arthritis, osteoporosis, and cardiovascular diseases. Exercise improves joint mobility, strengthens bones, and helps maintain cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases commonly observed in older adults.
Maintaining independence and quality of life
Physical fitness is crucial for maintaining independence and a high quality of life in older adults. Regular exercise improves balance, coordination, muscle strength, and flexibility, reducing the risk of falls and fractures. Maintaining physical fitness allows older adults to continue performing daily activities and enjoy an active lifestyle.
Reducing risk of falls and fractures
Physical fitness plays a significant role in reducing the risk of falls and fractures in older adults. Improved balance, muscle strength, and coordination resulting from regular exercise help prevent falls and minimize the risk of bone fractures, which are common concerns in older age.
Promoting Physical Fitness in Children and Adolescents
Encouraging physical fitness in children and adolescents sets the foundation for a healthy lifestyle and reduces the risk of various health problems later in life. Here are some strategies to promote physical fitness in younger individuals:
Encouraging active play and sports
Encourage children to engage in active play and participate in sports regularly. Encourage outdoor activities that involve running, jumping, and climbing. Additionally, enrolling children in organized sports teams can foster a love for physical activity and promote teamwork and social skills.
Incorporating physical activity into school curriculum
Schools can play a vital role in promoting physical fitness by incorporating physical activity into the curriculum. Physical education classes, recess breaks, and extracurricular sports programs can help children and adolescents achieve the recommended amount of physical activity each day.
Limiting sedentary behaviors
Limiting screen time and sedentary behaviors is crucial for promoting physical fitness in children and adolescents. Encourage children to engage in activities that involve movement instead of spending excessive time on screens. Setting limits on screen time and providing alternatives such as outdoor activities or hobbies can help promote physical fitness.
Physical Fitness for Different Population Groups
Physical fitness is beneficial for individuals of all ages and can be adapted to meet the needs of different population groups. Here are some considerations for physical fitness in specific populations:
Pregnant women and physical activity
Physical activity during pregnancy can have numerous benefits for both the mother and the baby. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting or continuing an exercise routine during pregnancy. Exercise recommendations may vary depending on individual circumstances, and certain activities may need to be modified or avoided.
Benefits of physical fitness in older adults
Physical fitness is crucial for maintaining health and independence in older adults. Engaging in activities that improve cardiovascular fitness, strength, balance, and flexibility can help older adults maintain a high quality of life and reduce the risk of age-related health issues.
Adapting exercise routines for individuals with disabilities
Physical fitness is possible for individuals with disabilities, and exercise routines can be adapted to meet their specific needs. Consulting with a healthcare professional or physical therapist can help determine suitable exercises and modifications to ensure safety and maximize benefits for individuals with disabilities.
Conclusion
Regular physical fitness is essential for disease prevention and overall well-being. Engaging in physical activity has numerous benefits, including a reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved mental health, enhanced cardiovascular health, and increased longevity. Adopting a physically active lifestyle and incorporating various types of exercises, such as aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises, can help individuals of all ages achieve and maintain physical fitness. Additionally, physical fitness plays a crucial role in preventing and managing various health conditions, promoting mental well-being, and improving quality of life in older adults. By promoting physical fitness in children and adolescents and adapting exercise routines for different population groups, we can ensure that everyone has the opportunity to enjoy the benefits of regular physical activity. Start prioritizing physical fitness today and reap the lifelong rewards it offers.




