Did you know that physical fitness plays a crucial role in maintaining your cardiovascular health? Staying active and engaging in regular exercise can greatly benefit your heart and overall well-being. In this article, we will dive deeper into the importance of physical fitness and how it can positively impact your cardiovascular health.
Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises, helps to improve your cardiovascular fitness. Engaging in activities like jogging, swimming, or cycling increases your heart rate, which strengthens your heart muscle. This, in turn, improves the pumping efficiency of your heart, allowing it to deliver oxygen-rich blood to all parts of your body more effectively. Not only does physical fitness enhance your heart’s ability to function optimally, but it also helps in reducing the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure. Ready to learn more about how you can enhance your cardiovascular health through physical fitness? Keep reading! and cardiovascular health are closely interconnected. Engaging in regular physical exercise can have numerous benefits for your cardiovascular system, including a lower risk of heart disease, improved blood circulation, decreased blood pressure, reduced risk of stroke, increased aerobic capacity, and enhanced heart and lung function. In this article, we will explore the importance of physical fitness for cardiovascular health, the different types of physical activities that promote cardiovascular fitness, how to design an effective fitness program, the benefits of physical activity on heart health, safety considerations and precautions, incorporating physical fitness into daily life, the role of nutrition in physical fitness, and the potential long-term health benefits of maintaining a consistent fitness routine.
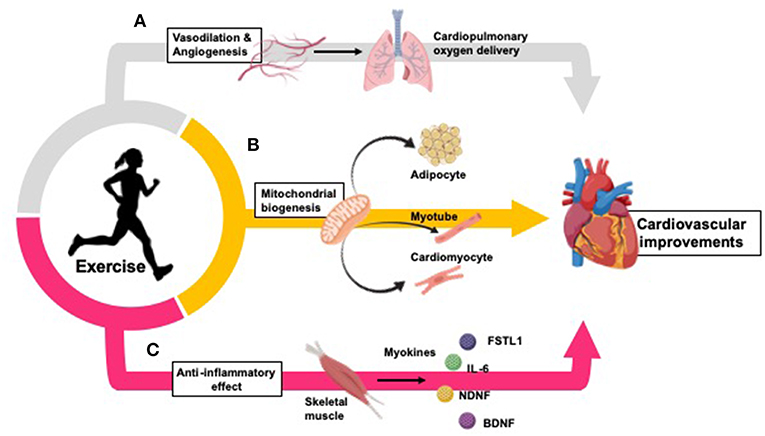
Introduction
What is physical fitness?
Physical fitness refers to the overall well-being and ability to perform physical activities without excessive fatigue. It includes several components, such as cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength and endurance, flexibility, and body composition. Achieving and maintaining physical fitness requires regular engagement in physical activities that target these different components.
Why is physical fitness important for cardiovascular health?
Cardiovascular health is crucial for overall well-being as it pertains to the health and functioning of the heart and blood vessels. Physical fitness plays a significant role in maintaining and improving cardiovascular health. Regular physical exercise strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases, and has numerous other positive effects on the body.
Benefits of Regular Physical Exercise
Lower risk of heart disease
Engaging in regular physical exercise has been shown to lower the risk of developing heart disease. It helps to reduce blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and maintain a healthy weight – all factors that contribute to a healthy heart. By incorporating cardiovascular exercises, strength training, flexibility and stretching exercises, as well as balance and coordination exercises into your routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease.
Improved blood circulation
Regular physical exercise improves blood circulation throughout the body. As you engage in cardiovascular exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the muscles, improving their ability to function. Improved blood circulation not only benefits the muscles but also enhances overall organ function and helps to remove waste products from the body more efficiently.
Decreased blood pressure
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Regular physical exercise has been shown to effectively lower blood pressure levels. By engaging in aerobic activities, strength training, and incorporating cardiorespiratory exercises into your routine, you can reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, promoting better overall cardiovascular health.
Reduced risk of stroke
Stroke occurs when the blood flow to the brain is interrupted, leading to brain cell damage or death. Regular physical exercise helps to reduce the risk of stroke by improving blood circulation, maintaining healthy blood pressure levels, and reducing the levels of LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) in the body. By including cardiovascular exercises and strength training in your fitness routine, you are taking proactive steps towards reducing your risk of stroke.
Increased aerobic capacity
Aerobic capacity, also known as cardiorespiratory fitness, refers to the ability of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems to deliver oxygen to the working muscles during prolonged exercise. Regular physical exercise improves aerobic capacity by strengthening the heart muscle, increasing lung capacity, and improving blood circulation. By engaging in activities that elevate your heart rate, such as jogging, swimming, or cycling, you can enhance your aerobic capacity and overall cardiovascular health.
Enhanced heart and lung function
Regular physical exercise strengthens the heart muscle, leading to improved heart function. As the heart becomes stronger, it pumps blood more efficiently, reducing the strain on the cardiovascular system. Additionally, physical exercise improves lung function by increasing lung capacity and enhancing the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. By engaging in activities that challenge the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, you can enhance heart and lung function, promoting better overall cardiovascular health.
Types of Physical Fitness Activities
Cardiovascular exercises
Cardiovascular exercises, also known as aerobic exercises, involve rhythmic movement of large muscle groups, such as the legs and arms. These exercises increase the heart rate and improve cardiovascular endurance. Examples of cardiovascular exercises include walking, running, swimming, cycling, dancing, and rowing. Engaging in these activities for at least 150 minutes per week is recommended for optimal cardiovascular health.
Strength training
Strength training exercises, also known as resistance training or weight lifting, involve working against resistance to build muscle strength and endurance. These exercises can be performed using free weights, weight machines, resistance bands, or body weight. Strength training not only improves muscle strength but also increases bone density and promotes a healthy body composition. It is recommended to engage in strength training exercises at least two days per week, targeting major muscle groups.
Flexibility and stretching exercises
Flexibility and stretching exercises involve moving the joints through their full range of motion, improving flexibility and joint mobility. These exercises can include static stretches, dynamic stretches, yoga, or Pilates. Flexibility exercises help to prevent injuries, improve posture, and enhance overall physical performance. It is recommended to perform flexibility exercises at least two days per week, focusing on the major muscle groups.
Balance and coordination exercises
Balance and coordination exercises help to improve stability and prevent falls. These exercises typically involve maintaining control and stability while performing movements that challenge balance, such as standing on one leg, practicing yoga poses, or using balance boards. Engaging in balance and coordination exercises can enhance proprioception, body awareness, and overall physical performance. It is recommended to perform balance and coordination exercises for at least two days per week.
Designing an Effective Fitness Program
Setting achievable goals
When designing a fitness program, it is essential to set achievable goals that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). By setting realistic goals, you can track your progress and stay motivated to continue with your fitness routine.
Choosing appropriate exercises
Selecting exercises that target different components of physical fitness is crucial for a well-rounded fitness program. Including cardiovascular exercises, strength training, flexibility and stretching exercises, as well as balance and coordination exercises, can help to improve overall fitness and cardiovascular health.
Creating a balanced workout routine
A balanced workout routine includes exercises that target different muscle groups and fitness components. It is important to incorporate cardiovascular exercises, strength training, flexibility and stretching exercises, as well as balance and coordination exercises into your routine to ensure comprehensive fitness development.
Progressive overload and variation
To continue seeing progress and improvement in physical fitness, it is essential to apply the principles of progressive overload and variation. Gradually increasing the intensity, duration, or frequency of your workouts helps to challenge your body and promote continual adaptation. Additionally, incorporating variety into your fitness routine can prevent boredom and plateaus.
Including rest and recovery days
Rest and recovery are just as important as exercise when it comes to maintaining a healthy fitness routine. Giving your body time to rest and recover allows for muscle repair and growth. It is recommended to include rest days in your fitness program, alternating high-intensity workouts with low-intensity activities or complete rest.
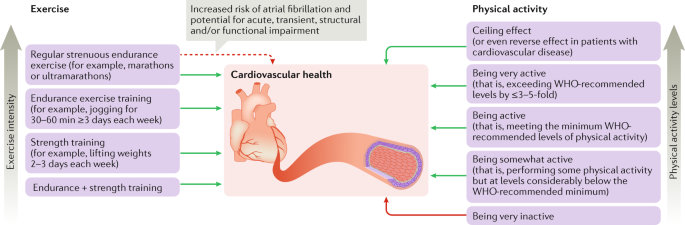
Cardiorespiratory Fitness Testing
VO2 max testing
VO2 max testing is a measure of the maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilize during intense exercise. It is often used to assess cardiorespiratory fitness levels and endurance. VO2 max testing involves performing a maximal exercise test while monitoring various physiological parameters, such as heart rate, oxygen consumption, and carbon dioxide production.
Submaximal exercise tests
Submaximal exercise tests are commonly used to estimate an individual’s aerobic fitness level without performing maximal exertion. These tests involve exercising below the maximum effort level while monitoring heart rate response, breathing rate, and other physiological parameters.
Field tests and functional assessments
Field tests and functional assessments are alternative methods to assess cardiorespiratory fitness without the need for specialized equipment. These tests typically involve specific exercises or activities, such as the 1.5-mile run/walk test or step tests, to assess aerobic fitness levels.
Effects of Physical Activity on Cardiovascular Health
Improved heart health
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, and reduces the risk of various cardiovascular diseases. Engaging in physical activities that elevate your heart rate, such as jogging, cycling, or swimming, promotes better heart health and overall cardiovascular fitness.
Reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases
Regular physical exercise has been shown to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, and hypertension. By engaging in aerobic exercises, strength training, and maintaining a balanced fitness routine, you can significantly lower your risk of these conditions.
Lower resting heart rate
Regular exercise has been shown to lower resting heart rate, indicating better cardiovascular fitness. A lower resting heart rate means that the heart does not have to work as hard to pump blood, reducing the strain on the cardiovascular system.
Decreased cholesterol levels
Physical exercise can help to reduce LDL cholesterol levels (“bad” cholesterol) and increase HDL cholesterol levels (“good” cholesterol) in the body. By incorporating cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and maintaining a balanced diet, you can improve your cholesterol profile and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Improved blood sugar control
Regular physical exercise helps to improve blood sugar control by increasing insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to better utilize glucose. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes.
Enhanced weight management
Engaging in regular physical exercise is an effective way to manage body weight and prevent obesity. Physical activity helps to burn calories, increase metabolism, and build lean muscle mass, contributing to overall weight management and healthy body composition.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
Consulting with a healthcare professional
Before starting any new exercise program, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or concerns. They can provide guidance on suitable physical activities and help to identify any potential risks or limitations.
Importance of proper warm-up and cool-down
Including a proper warm-up and cool-down in your fitness routine is essential for injury prevention and optimal performance. A warm-up prepares your body for exercise by increasing blood flow to the muscles and increasing joint mobility, while a cool-down allows your body to gradually return to its resting state and helps to prevent post-exercise muscle soreness.
Using appropriate equipment and gear
When engaging in physical activities, it is crucial to use proper equipment and gear to ensure safety and reduce the risk of injury. This may include wearing appropriate footwear, using protective gear such as helmets or knee pads, or using equipment correctly and according to safety guidelines.
Avoiding overexertion and pushing beyond limits
While it is important to challenge yourself during workouts, it is equally important to listen to your body and avoid overexertion. Pushing beyond your limits can increase the risk of injury or fatigue, so it is important to exercise within your comfort zone and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
Recognizing signs of injury or illness
It is crucial to pay attention to any signs of injury or illness during physical activity. If you experience prolonged or severe pain, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, or any other concerning symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention and stop exercising until cleared by a healthcare professional.
Incorporating Physical Fitness into Daily Life
Finding enjoyable activities
Incorporating physical fitness into your daily life is more likely to be sustainable if you find activities that you enjoy. Whether it’s dancing, hiking, swimming, or playing a sport, choosing activities that you have fun doing will help to make physical activity a regular part of your routine.
Setting realistic time constraints
Many people find it challenging to fit exercise into their busy schedules. However, even small amounts of physical activity can make a significant difference in your health. Setting realistic time constraints and finding ways to incorporate short bouts of exercise throughout the day, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator or going for a brisk walk during lunch breaks, can help you meet your fitness goals.
Making physical activity a habit
Consistency is key when it comes to physical fitness. Making physical activity a regular habit can significantly increase the likelihood of long-term adherence. Choose a specific time of day and schedule your workout like any other appointment or commitment.
Incorporating exercise into daily routines
Finding creative ways to incorporate exercise into daily routines can help to make physical activity a seamless part of your daily life. For example, biking or walking to work or running errands on foot can provide opportunities to be active while accomplishing daily tasks.
Engaging in active hobbies or sports
Engaging in active hobbies or sports is a great way to combine physical activity with leisure time. Whether it’s joining a recreational sports league, taking up a dance class, or gardening, finding activities that you enjoy can make physical activity more enjoyable and fulfilling.
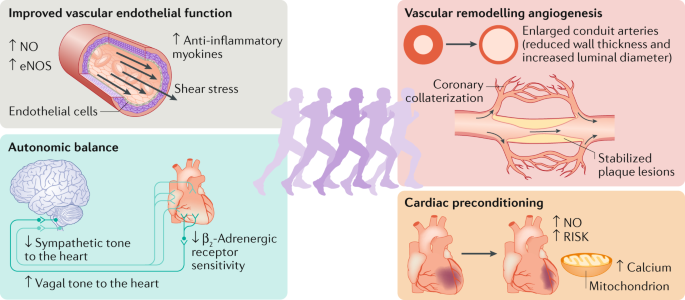
Nutrition and Physical Fitness
Importance of a balanced diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in supporting physical fitness and cardiovascular health. Following a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats, provides the necessary nutrients to fuel your exercise routine and promote overall wellness.
Fueling the body for optimal performance
Proper nutrition before, during, and after exercise is essential for optimal performance. Consuming a combination of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats before a workout provides energy, while staying hydrated and replenishing electrolytes during exercise helps to maintain performance. After exercise, consuming a balanced meal or snack that includes proteins and carbohydrates promotes muscle recovery and replenishes energy stores.
Hydration and electrolyte balance
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining optimal physical performance and preventing dehydration. It is important to drink fluids throughout the day, particularly before, during, and after exercise. Additionally, maintaining electrolyte balance by consuming foods or beverages that contain sodium, potassium, magnesium, and other electrolytes is important for proper muscle function and overall hydration.
Nutrition for muscle recovery
After engaging in physical exercise, proper nutrition is essential for muscle recovery and growth. Consuming an adequate amount of protein, along with carbohydrates, helps to repair muscle tissue and replenish energy stores. Including sources of protein, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, or plant-based proteins, in your post-workout meals or snacks can support muscle recovery.
Supplements and their role in physical fitness
Supplements can be a helpful addition to a healthy diet and fitness routine but should not replace whole foods. Certain supplements, such as protein powders or branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), may support muscle recovery and performance. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any supplements to ensure they are appropriate for your individual needs.
Conclusion
Physical fitness plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving cardiovascular health. Engaging in regular physical exercise has numerous benefits, including a lower risk of heart disease, improved blood circulation, decreased blood pressure, reduced risk of stroke, increased aerobic capacity, and enhanced heart and lung function. By incorporating different types of physical activities, designing an effective fitness program, understanding the effects of physical activity on cardiovascular health, considering safety considerations and precautions, incorporating physical fitness into daily life, and focusing on nutrition, you can promote better cardiovascular health and overall well-being. Striving for a balanced and consistent fitness routine and making physical activity a habit are key to reaping the potential long-term health benefits of regular exercise. So lace up your sneakers, grab your water bottle, and get moving – your heart will thank you!

